Social-Ecological and Technological Factors Moderate the Value of Urban Nature
Citation
Keeler, B. L., Hamel, P., McPhearson, T., Hamann, M. H., Donahue, M. L., Meza Prado, K. A., … & Wood, S. A. (2019). Social-ecological and technological factors moderate the value of urban nature. Nature Sustainability, 2(1), 29-38.
Abstract
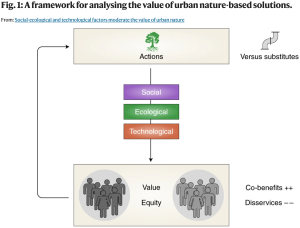
Urban nature has the potential to improve air and water quality, mitigate flooding, enhance physical and mental health, and promote social and cultural well-being. However, the value of urban ecosystem services remains highly uncertain, especially across the diverse social, ecological and technological contexts represented in cities around the world. We review and synthesize research on the contextual factors that moderate the value and equitable distribution of ten of the most commonly cited urban ecosystem services. Our work helps to identify strategies to more efficiently, effectively and equitably implement nature-based solutions.