The Benefits of Nature Experience: Improved Affect and Cognition
Citation
Bratman, G. N., Daily, G. C., Levy, B. J., & Gross, J. J. (2015). The benefits of nature experience: Improved affect and cognition. Landscape and Urban Planning, 138, 41-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.02.005
This study looked at how spending time in nature affects mood and thinking. Sixty people were randomly assigned to take a 50-minute walk either in a natural area or in an urban setting near Stanford, California. Before and after their walk, they completed tests measuring their emotions and thinking skills.
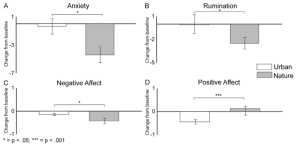
People who walked in nature felt better afterward. They had less anxiety and negative thinking, and their positive mood stayed about the same. They also did better on a memory test that measures how well people can hold and work with information at the same time.
In short, even a short walk in nature can improve both mood and thinking compared to walking in a city. These results add to what we know about the mental benefits of spending time outdoors and lays the foundation for future research on why nature has these positive effects.
Abstract
Highlights
- Nature experience produced clear benefits for affect (e.g., decrease in anxiety and rumination).
- Nature experience produced some benefits for cognition (complex working memory span task).
- Supports the idea that exposure to natural greenspace can improve affect and cognition.
This study investigated the impact of nature experience on affect and cognition. We randomly assigned sixty participants to a 50-min walk in either a natural or an urban environment in and around Stanford, California. Before and after their walk, participants completed a series of psychological assessments of affective and cognitive functioning. Compared to the urban walk, the nature walk resulted in affective benefits (decreased anxiety, rumination, and negative affect, and preservation of positive affect) as well as cognitive benefits (increased working memory performance). This study extends previous research by demonstrating additional benefits of nature experience on affect and cognition through assessments of anxiety, rumination, and a complex measure of working memory (operation span task). These findings further our understanding of the influence of relatively brief nature experiences on affect and cognition, and help to lay the foundation for future research on the mechanisms underlying these effects.
Related Media
- Nature May Be Key to Strengthening Our Attention (November 28, 2023)