Results From an 18 Country Cross-Sectional Study Examining Experiences of Nature for People with Common Mental Health Disorders
Citation
Tester-Jones, M., White, M. P., Elliott, L. R., Weinstein, N., Grellier, J., Economou, T., … & Fleming, L. E. (2020). Results from an 18 country cross-sectional study examining experiences of nature for people with common mental health disorders. Scientific reports, 10(1), 19408.
Abstract
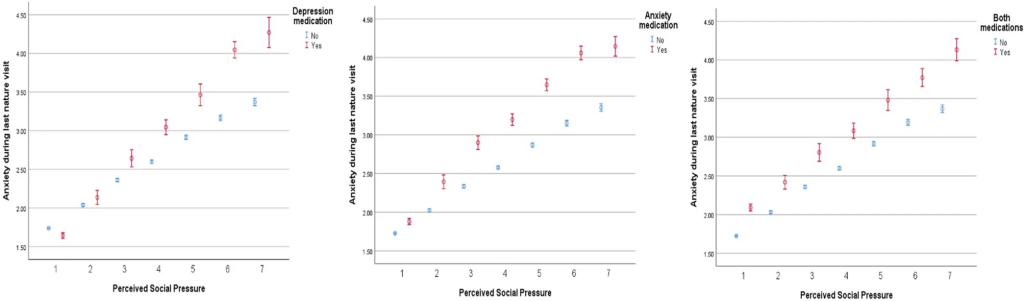
Exposure to natural environments is associated with a lower risk of common mental health disorders (CMDs), such as depression and anxiety, but we know little about nature-related motivations, practices and experiences of those already experiencing CMDs. We used data from an 18-country survey to explore these issues (n = 18,838), taking self-reported doctor-prescribed medication for depression and/or anxiety as an indicator of a CMD (n = 2698, 14%). Intrinsic motivation for visiting nature was high for all, though slightly lower for those with CMDs. Most individuals with a CMD reported visiting nature ≥ once a week. Although perceived social pressure to visit nature was associated with higher visit likelihood, it was also associated with lower intrinsic motivation, lower visit happiness and higher visit anxiety. Individuals with CMDs seem to be using nature for self-management, but ‘green prescription’ programmes need to be sensitive, and avoid undermining intrinsic motivation and nature-based experiences.