Nature and Human Well-Being: The Olfactory Pathway
Citation
Bratman, G. N., Bembibre, C., Daily, G. C., Doty, R. L., Hummel, T., Jacobs, L. F., Kahn, P. H., Olvera Alvarez, H. A., … & Spengler, J. D. (2024). Nature and human well-being: The olfactory pathway. Science Advances, 10(20), eadn3028. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn3028
 The world’s atmosphere and ecosystems are changing rapidly, creating new challenges for human health and well-being. One often-overlooked part of this story is our sense of smell (olfaction). Smell can influence many aspects of our lives, including how we feel, how we think, what we eat, how we manage stress, etc. Breathing in different scents can even influence inflammation in the body.
The world’s atmosphere and ecosystems are changing rapidly, creating new challenges for human health and well-being. One often-overlooked part of this story is our sense of smell (olfaction). Smell can influence many aspects of our lives, including how we feel, how we think, what we eat, how we manage stress, etc. Breathing in different scents can even influence inflammation in the body.
This paper looks at how natural scents impact our well-being. Drawing on research from health, social, and natural sciences, the authors present four main agreements about the role of smell in the environment and a framework showing how natural scents can contribute to well-being. The authors also discuss how this knowledge can guide better policies and land-use decisions to protect natural smellscapes that support human health and, in time, planetary health.
Abstract
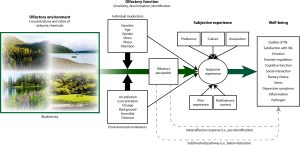
The world is undergoing massive atmospheric and ecological change, driving unprecedented challenges to human well-being. Olfaction is a key sensory system through which these impacts occur. The sense of smell influences quality of and satisfaction with life, emotion, emotion regulation, cognitive function, social interactions, dietary choices, stress, and depressive symptoms. Exposures via the olfactory pathway can also lead to (anti-)inflammatory outcomes. Increased understanding is needed regarding the ways in which odorants generated by nature (i.e., natural olfactory environments) affect human well-being. With perspectives from a range of health, social, and natural sciences, we provide an overview of this unique sensory system, four consensus statements regarding olfaction and the environment, and a conceptual framework that integrates the olfactory pathway into an understanding of the effects of natural environments on human well-being. We then discuss how this framework can contribute to better accounting of the impacts of policy and land-use decision-making on natural olfactory environments and, in turn, on planetary health.
Related Media
- How the smells of nature can affect human well-being (May 29, 2024)
- How do the smells of nature affect well-being? A call for more research. (May 23, 2024)
- Nature’s scents linked to improved health and well-being (May 16, 2024)