A Plasma Display Window?—The Shifting Baseline Problem in a Technologically mediated Natural World
Citation
Kahn Jr, P. H., Friedman, B., Gill, B., Hagman, J., Severson, R. L., Freier, N. G., … & Stolyar, A. (2008). A plasma display window?—The shifting baseline problem in a technologically mediated natural world. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 28(2), 192-199.
Abstract
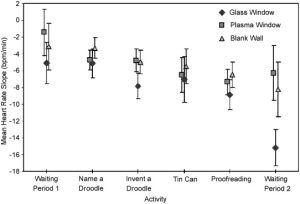
Humans will continue to adapt to an increasingly technological world. But are there costs to such adaptations in terms of human well being? Toward broaching this question, we investigated physiological effects of experiencing a HDTV quality real-time view of nature through a plasma display “window.” In an office setting, 90 participants (30 per group) were exposed either to (a) a glass window that afforded a view of a nature scene, (b) a plasma window that afforded a real-time HDTV view of essentially the same scene, or (c) a blank wall. Results showed that in terms of heart rate recovery from low-level stress the glass window was more restorative than a blank wall; in turn, a plasma window was no more restorative than a blank wall. Moreover, when participants spent more time looking at the glass window, their heart rate tended to decrease more rapidly; that was not the case with the plasma window. Discussion focuses on how the purported benefits of viewing nature may be attenuated by a digital medium.